You are reading this article it means you are interested person in the field of quality engineer. There are lot of pain point of the quality engineer in the organization.
- No career growth and knowledge growth
- Only doing inspection of parts on the line
- No decision-making authority.
- No involvement in cross functional team
- No involvement in documentation, standardization, and improvement.
In this article we will cover everything you need to know about the quality engineer.
This is the perfect and complete guide for every quality engineer that you must read.
I already covered the topics which is beneficial for every quality engineer to stand in interview, and you can be able to answer every question of interviewer.
After all, many of you already start working in Quality Field. And you wanted to know all concepts and the meaning of a true Quality Engineer.
This article is the master process, which every quality engineer will gone through. Try to learn all tools and skills in detail what I have mention in this article.
What is a Quality Engineer and why are they important?
A quality engineer is a professional who understands the product, process, and service quality. He can develop the operation of quality systems and documentation.
A quality Engineer is very important in an organization because he knows the concept related to data analysis, techniques, and methodology to apply to problem-solving and improving the product, process, and management system.
In this guide, you will find the roadmap, tools, skills, and concepts. So that you will be able to start progress in your career by following the steps.
So, without further delay, here are the steps:
Step #1: The Start
Let’s try to understand the beginning from where you start your job in the company.
You have completed your graduation as Bachelor degree. in the field of Mechanical or Automobile or any other field.
Then you visit the city where industries are located and apply for the job. You will get the job in one of the manufacturing companies as a fresher role.
As you are reading this article means you are selected to work in the quality department.
Now as a fresher you only have knowledge of the academic what you have learned in your college days. But industry is bit different as compared to work culture and experience.
I will start from the beginner level.
Forget about your current role now and just focus on understanding the company first.
Step #2: Understanding Company
Manufacturing company is running and making profit base on the products they are producing and selling to the customers.
The manufacturing industries play a important role in countries progress. A lot of businesses comes under manufacturing segment.
Here are the five types of manufacturing industries that are predominant in the market.
- Metal Manufacturing
- Apparel and textile.
- Gadgets, computers, and electronics
- Oil, chemicals & Plastics.
- Food Production
In our case let’s take an example, assume our company is producing the gears and provide those gears to the customer for example Tata Motors or Mahindra or Volkswagen or Bosch or any other company.
Now as we are producing the parts and supply those parts to the customer. To make this all happen we need people and a system. And company is now having a system in which all peoples are working.
Therefore, every company has a departments and a set of peoples are working in the respective departments.
Organizational Knowledge
Yes, this is the step where you must have organizational knowledge such as the organizational structure. What are the departments in your company and who is leading those departments?
Also importantly what is exactly organizational knowledge and its type, let’s see below.
What is organizational knowledge?
It is the knowledge of an organization you get from collective experience or from the individual experience of the person. This knowledge can be used to achieve the organizational goals & objectives.
The organization’s knowledge includes employee handbooks, company standards, product knowledge, manuals, intellectual property, customer communications, and lessons learned from success and failure.
Organizational knowledge is very important because, it will help you in decision making, innovation, learning, and problem solving.
So basically every quality engineer has the below types of organizational knowledge.
Types of organizational knowledge

Tacit Knowledge
Explicit Knowledge
Individual Knowledge
Collective Knowledge
Departments
Let’s understand now how many departments are in the company.
Departments in organizations
Generally every company has a common departments such as,
- Purchase Department
- Engineering Department
- Human Resource Department
- Quality Department
- Production Department
- Logistics Department
- Sales/customer Department
- Maintenance Department
- Finance Department
- IT Department
- Also can be many more.
We already covers all important departments.
Now understand the function and role of each department in short,
Purchase/Procurement Department
First Purchase Department: Purchase is responsible for the procurement activity. This department will provide you the things that are important for production and operations.
For example if you need one of the measuring instrument then you raise a request to purchase department. Then they find out the suppliers in the market and get the quotation from them. Among those supplier whichever is best they purchase that equipment and provide it to you. Hope you got the idea of purchasing function.
Engineering Department
Next we have a Engineering Department: This department is responsible for all the activity related to new product development. Engineering department will be in contact with customer to developed the new product in the organization and after final submission and smooth working they handover all the activities to production department.
Production Department
So Production Department: Production department is responsible for all the activities required to manufactured the product. Production department is the heart of manufacturing company. The activities of production are operating machines, manpower handling, material, manufacturing planning and many more.
Logistics Department
Next we have a Logistics Department: Logistics will be responsible for the supply chain activities. Considering the invoicing, material inward and delivery and many more.
Sales/Customer Department
Then we have Sales/customer Department: Sales will be responsible to get the new business from the market. They are in contact with other industry that how they can get the business from customers.
Maintenance Department
The Maintenance Department will be taken care of all the machinery and electrical systems of the company.
Accounts and Finance Department
The Finance Department will take care of all money related topics. Accounts and Finance are more what similar in nature.
IT Department
The IT Department will be taken care of all IT hardware (Laptop, computers, servers) and IT software’s.
You thing where is my department, lets discuss the quality department now.
Quality Department
You must know the detailed structure of quality department as you are selected to work in quality department.
Quality Department consist of sub departments, or we can say sub functions taken care by small teams,
Which is
- Supplier Quality
- Production Quality
- Customer Quality
- New Product Development Quality
- QMS
Supplier Quality
To check and maintain the quality of incoming parts received from supplier are the prime responsibility of supplier quality. Below are some responsibilities of supplier quality,
- Check the incoming part on sampling basis and provide approval
- Monitor the supplier rejection data
- Monitor the supplier performance
- Fill and maintain the inspection reports, formats and documents.
- Supplier communication on resolution of supplier issues
- Do the supplier audit at define frequency or audit plan.
Production Quality:
After approval by the supplier quality, the incoming parts goes to the production line for further processes. The operation we called as in-process activity.
Therefore the quality of the In-process parts are verify and control by production quality function.
The responsibilities of production quality is,
- Check and provide approval of in-process parts
- Doing the inspection of first part and in-process parts to control the quality and detect the not ok part on the line.
- Fill and maintain the in-process quality check sheets and records.
Customer Quality:
When we done our manufacturing and final product is as output. Then the customer quality will check and verify the product as per specification and customer requirement. And then the parts are deliver to the customer.
The tasks or activities of customer quality team is as below,
- Doing final pre-dispatch inspection, dock audit and qualify the parts
- Doing customer communication related to product quality and failures.
- Resolution of customer complaints, warranty claim etc. using problem solving tools.
- Create and implement action plan for the customer complaint resolution and immediate action to reduce the consequences of the defects.
New Product Development Quality:
Check and validate the quality of new product in the organization is the responsibility of the new product quality.
When we say new product it means the complete product is taken care by the engineering or NPD team. The NPD quality team is there to support engineering team.
The responsibilities of the NPD quality team is as below,
- Check and maintain the quality of new products
- Create and maintain the PPAP documentations
- Involved in APQP process to do the activities related to quality functions.
- Create initial studies, inspection and verification records.
QMS:
Full form of QMS is Quality Management System. It is the process of creating and maintaining the QMS system in an organization. Which is mean all functions are performing according to standard guidelines of automotive industries.
The responsibilities of the QMS team is,
- Document controls
- Audit the product and process using guidelines provide by standards.
- Create culture of system as per the IATF or QMS standard.
- Perform internal audit of all departments to check weather all are working as per standards or not.
- Responsible to face the External customer or third party audit.
Up-to here you have understood the organization structure in brief. The quality department we discussed in little bit detailed.
Next topic is the documentation, now the Roadmap to learn the document.
Step #3: Product and Process
If you want success as a competent quality engineer, then you must have a piece of good knowledge of the product and process in your organization.
Basically, when you start your career in the Quality field, you start with product knowledge.
1. Product
The product is nothing but the final output of your company. It can be anything Physical or virtual. In Manufacturing the final outcome such as the car, axel, door, clutch, gear, Rod, many more physical part, etc. In the Software industry, it is a software.
A product is any item or service you sell to serve a customer’s need or want.
Now the best part is how you will get the product information.
You should understand the product by understanding customer requirement. What are the characteristics we are going to achieved on our product so that this product is meet our customer fitment?
- Know the product characteristics or customer requirement. Product drawings (Engineering Drawings)
- Which material was used for it… what are the Chemical elements used in the material and their functional requirements.
- What are the defects in the products?
- What is the function of this product (Fitment at next process / at customer end)
- How we are handling the product (Packaging/storage)
Product knowledge is very crucial before going into process depth.
2. Process
Every quality engineer should know about the processes in the industry which he is working with.
What is Process?
Let’s see from the definition perspective. The process is the set of activities where inputs convert to output.

So, to get expertise in the process, You need to go through the on-the-job training process. Please learn how the raw materials or incoming parts pass through our manufacturing processes and how the outcome is produced.
Work as an entry-level unskilled Graduate Engineer Trainee (GET). Learn different types of equipment and know what kind of product are being made and how.
Spend your break time just by walking around the assembly line or process line. Talking to people who are in charge of other operations. And to find out what needs to done in each process step.
To learn more, do a job in the factory/industry that is making very complicated products from many materials.
for example, Automotive plants, use almost every manufacturing process at some point.
- Welding Process
- Sheet metal forming process
- Machining
- Injection molding process
- Assembly Processes
- Etc.
Here is what you need to learn from a process point.
- Process flow: How processes are linked
- What are the steps in the processes
- Process characteristics: These are responsible to get our product as per requirement
- Operating procedures (SOP)
- Inspection methods: Different types of equipment and instruments
- Documentation on process lines and what is the purpose of them
- Process standards and process yields and outputs.
Step #4: Documentation, Tools and Techniques
Coming to the documentation topics, I have listed below frame for you to learn at beginner level,
- Quality Core Tools
- Ground level documents and formats
- QMS (IATF & ISO standard) overview
- Problem solving tool’s
Product Development Cycle | Quality Core Tools
Don’t be confused, I will explain these all documents starting from zero with the flow of product development cycle.
Business starts with the customer. Customer is looking for the supplier in the market for, who can provide the parts to me?.
Customer do the market research and he found that your company is providing the similar product. Then he contacts to your sales department.
Your company got the request from customer. It means you have received the Enquiry / RFQ (Request For Quotation) request from customer.
Now the company cross functional team among all departments are do the feasibility check of the customer & Product requirements.
P.S.: Two conditions you must understand here.
First cases customer provides the drawing and ask to manufacture the product.
Second case is customer gives you requirements and ask you to provide the product. Here the product design and manufacturing both responsibility of supplier.
Back to the topic, you got the enquiry from customer then you do the feasibility check, prepared a quotation, and send back to the customer.
If customer agreed, he would give you approval. It means the program are now awarded by customer.
From here the actual development cycle started.
Development Cycle
I hope up-to this the overall concept is clear.
The development cycle we called as APQP process (Advanced Product Quality Planning).
P.S.: In automotive industry two type of development cycle. This is because the automotive market is globally spreads. Two groups are there in automotive industry. One is AIAG (Automotive Industry Action Group) and other is VDA (German Automotive Association).
Both have their development cycles, AIAG used the APQP process and VDA used the VDA-MLA process.
- APQP: Advanced Product Quality Planning (3rd Edition 2024)
- MLA: Maturity Level Assessment
Don’t be confused with these terms, both methods work with same approach or principle.
Let’s understand the process, for now you must understand the process in basic way.
- First, we do product design.
- Then we do process design
- Next, we need to validate the product and process to check the product and process meets the requirement or not.
- Lastly, we do the production trail to check the parts possible to manufactured at required production rate or not with good quality.
Now let’s understand the APQP process,
APQP Process
The APQP process has a 5 phases of development.
- Plan and Define
- Product Development
- Process Development
- Product and Process Validation, Production
- Feedback assessment and corrective action
Further I will explain you the process of development. Each phase has the documents as the output of the phase. You must understand the reason behind each documents. I will explain you which document needs to create at which stage and how you can create.
Let’s start from phase 1: Plan and Define.
Phase 1: Plan and Define
The purpose of the plan and define stage is to understand the customer expectation and customer requirement. What we are going to developed and how we can do?
For this activity we need some inputs data, such as,
- Customer voice: What customer want. Customer provide us the requirements. For example customer give you drawings, materials specification, customer interface requirement etc.
- If the design is your then customer provide you the functions of the product they want, provide you the packaging in the vehicle where product will be fitted. Other requirement of the product such as temperature requirement, weight requirement, mechanical properties of the product etc.
- In some cases market research data, warranty and quality data is the inputs for us.
There are lot of requirement we need to understand in the plan and define phase.
Then based on the above inputs, you have now some information with you regarding the product you will be developed.
The information you have is Design goals (What we need to design), Quality Goals (What quality requirement by customer), Initial or draft process flow chart, some preliminary product and process characteristics, etc.
Timing Plan
One more important activity we do in plan and define phase is to prepare a Timing Plan.
There is lot of activity we need to perform while developing a new product. And those activities are done by various teams in the organization. Therefore one master timing plan is created in first stage.
This timing plan includes the overall time required to develop a product, many activities description, when these activities are plan vs actual status and who is responsible to the activities.
The Timing plan is the master document of all APQP process. Some companies follow the project management software to track those activities and plan the APQP process. Some small and medium companies plan and track those activities in excel spreadsheet.
Ok, this is all about the first phase of development.
Now the 2nd Phase is Product Design and Development.
Phase 2: Product Design and Development
Now you have the output of the plan and define phase. Use this information to create your product design. It means all customer engineering requirements will be consider and design the product.
It also involves the design reviews and do the risk analysis of the design. The manufacturability, feasibility, reliability of the product design is review in this stage.
You will know the product specifications in this stage. Therefore below documents are the output of the Product Design and Development Phase.
DFMEA:
We must do the product design risk analysis, it means we need to do the Design Failure Mode Effect Analysis in this stage to find out the potential design failures and correct the design.
Design Verification and Design Reviews:
During development process, regular meetings are carried out to do the design review and verifications. It includes to review that our design meets the customer requirements or not. Functional interface requirements, texts verification and all these activities are part of design review and verifications.
Prototype control plan:
This control plan includes what dimensions we will measure and how we will control that during the prototype creation.
Actual Drawings and specifications:
The drawing are ready in this stage therefore you have now the complete product drawing and product specifications
So now you can understand what activities and documents are created in the phase 2 of product design and development.
2nd phase completes and before going to 3rd phase there is called a Gate here. When every phase is completed then there is a Gate review of this phase. Gate Review means the review of all the output of the phase and is it completed within time as per timing plan and all documents and outputs are ok or not.
Once the gate review pass then the program move to next phase.
Phase 3: Process Design and Development
Let’s jump to 3rd Phase Process Design and Development.
Recap: We do planning in 1st phase then we do the product design in the 2nd phase.
Now our job is to do the manufacturing of the product as per drawing specification and customer requirement.
For that we should ensure that our manufacturing system is well developed.
Therefore the activity of the process design and development includes to do the Floor plan layout, tooling, machine and equipment installations, Process flow chart and PFMEA.
It means all the activities or setup related to manufacturing line and documentation is done in the process design and development phase.
Packaging also covers in this step, so that our designed product is manufactured in correct way, without having a defect on the line.
This phase ensures all manufacturing line is working as per standard documents and work instruction as per control plan.
The output of the Process design and development step is,
- Process Flow chart
- Floor Plan Layout
- PFMEA
- Process Characteristics
- Pre-launch control plan
- Work instructions
- MSA plan
- SPC plan
- Packaging standards & specifications
Here your 3rd phase completes, then again it should pass the gate review.
Next
Phase 4: Product and Process Validation, Production.
This phase is important to validate our design, either process or product design.
How you are going to validate product and process then?
We can validate our product and process by going through the production run. It means we will do the production of our parts and check that we follow the process flow chart and control plan, work instruction to produce the parts. The final product is according to drawing specifications.
If any problem in the production run then investigate and improve the process before regular production.
This step is very important in terms of validation and documentation. Because all documents are also review in this step.
You think why?
Because the PPAP is also conduct in this stage.
Validation Phase
Let’s understand product and process validation phase in detail,
We do the production run, therefore all process is work as per process flow chart define. Then the control plan and work instructions are also support to do the operations.
Coming back to check the product as per specification or not, we need Measurement system. So the MSA is also done as per plan in 3rd Phase. Then we check our final output and do the capability study i.e. SPC.
In short this is to check that are we producing the parts within acceptable or define limit by the customer or not.
In this way the SPC is also done, which called as process capability study.
Up-to this step we already have lot of documents prepared. And now final customer approval is needed which is nothing but the PPAP (Production Part Approval Process).
To provide the approval customer will review and validate all the documents and production process, and then give you the approval.
Once it all done, then the Quality sign-off is done and the product and process is now handover to the production team from the engineering department.
Now the in-process quality and customer quality will take care of all part and process.
Still we have one phase pending which is phase 5 Feedback assessment and corrective action.
Phase 5: Feedback assessment and corrective action
This phase is a continuous journey where all additional improvement in the part and process is taken care by.
Which basically includes that reduce the process variation, improve customer satisfaction, improved the delivery and services.
Also use the lesson learnt and best practices in the program for continual improvement.
Now the development phase is done, you have understand all the documentation required in the development stage related to quality and overall approach.
You know the naming of documents, and where those applies in organization.
In summary you understood the process of below documents,
Quality Core Tools
Next is ground level documentations,
Ground level documentations
Once the project handover from development to the production team then production quality will take care all things.
Incoming Process
It comes with starting point as incoming inspection. We need raw materials or incoming child part to become a final customer part or assembly later.
Therefore it is important to verify and check the incoming part. Here the supplier quality will take care of the incoming inspection.
As a quality engineer you must know the inspection of incoming parts?. Every inspection or action in the organization based on standards.
Therefore the incoming inspection reports are the key record we need to fill after parts check.
The incoming parts check based on the control plan. You must know the control plan document here.
Then how many parts will check in each lot or batch received from customer. This is something you must know. The sampling plan is usually standard for how many parts received and how many parts we need to check to qualify the batch.
Also if there is any defect found by you then you must filled the defect sheet and communicate the defect to the supplier through mail. And open the customer complaint for those respective supplier.
Then immediate take action on supplier by doing follow-up to solve the complaint by the process of 8D method.
8D method is the problem solving tool used by the organizations. You must learn the 8D also.
This is all about the incoming.
Production Process
The parts then go on manufacturing line or process. Here the production quality plays a role.
Inspection & Control Plan
The production quality will do the inspection of in-process production parts. This inspection includes the first part inspection and in-process inspection.
Here also as a quality engineer you must know which dimension we need to check at specific station. And also know the control plan. Are we doing the inspection of correct dimension as per control plan or not.
Then you must know about the handling of instrument and for each method are we using correct instrument or not.
You are now able to fill the inspection record then if any dimensions you find not ok, it is recommend to stop the production find out the problem correct the problem with production team and give the approval again to start.
This method you can say as quality control job. Here you control the product quality by identifying the problem and correct it to maintain the quality.
SPC & MSA
You also need to learn the tools and techniques to control the quality of products such as SPC (Statistical Process Control).
The parts of SPC is control charts and capability study you must learn to become quality expert.
The purpose of SPC is to check our process variation, which means is our produce parts are within specification band or not. And based on that you will find that your process is capable to produce the ok parts consistently or not.
Before the SPC you must do the MSA (Measurement System Analysis). MSA is the process to check the variation present in measurement system.
The measurement system consist of the man, measurement equipment and parts. You must learn the Measurement System Analysis, where usually you need to perform the MSA studies. Such as Gage R&R, Attribute MSA, Linearity, Bias, Stability study.
Once you learn this means you can now understand the measurement system. If your measurement system is good then you will do the SPC study i.e. capability study.
Just follow the SPC implementation cycle and do the study accordingly.
In the SPC you need to check the parts and note down the observations sheet and get the results using calculations. Now a days it is done using excel spreadsheet and you will get the final result directly.
Base on the results you then decides whether you need to take some actions to improve your process or not.
Again one thing you must learn as a quality engineer is the process knowledge. You must learn how the process works? What are the process characteristics?, and process basics. This will help you to build more authority in your field and your value.
That’s it about the production quality ground documents you can learn.
Next the part moves to customer.
Customer
Customer Quality will take care of those parts. As a quality Engineer you must have a good communication skill to talk with customer.
There is also need to know all customer requirement related to product. Quality Engineer should know the product function at customer end.
This will comes to what customer wants? And what our key dimensions are needed for customer assembly and function purpose.
You must have skill of problem solving. Once the customer complaint / customer claim occur then you should communicate with customer to resolve the issues as early as possible to avoid the customer line stoppage.
This is more important from management point of view, because this will impact the business and company image.
Therefore customer quality is the focus point to the management.
Again as documentation point of view quality engineer know all problem solving tools, such as 8D methodology, QC story problem solving, 5-Why analysis, 7QC tools etc.
Customer complaint handling is important skill. You should prepare report and submit to the customer and close the complaint after verifying the effectiveness of action plan.
Sometimes the deviation management also need to do for negotiation and customer communication regarding hold parts.
QMS (IATF & ISO standard) overview
The Quality Management System is followed by overall company. And each department have their own QMS documents. Similar to Quality Departments have their own set of documents.
As a Quality Engineer you should understand those documents and formats. This is because when there is audit, you should present those documents to the auditor.
The basics of QMS documents is, There is a Standards like ISO & IATF.
When your company is manufacturing the non-automotive components then the ISO 9001:2015 standard is applicable.
If your company is manufacturing the automotive components or assembly then the IATF 16949:2016 standard is applicable.
Now this standard is a manual, and there are some chapters in it, we called as Clauses.
Each clauses has some requirements. Which says that what you should do and what is mandatory by the standard.
Those requirements are implemented in the organization in the form of documents, procedures and formats. That’s it.
You just need to understand your department documents and format at initial level. But if you want to work in QMS then you should learn all QMS standard and their requirement.
One more topic in the QMS is the Audit.
Audit
As a quality engineer you should know what is Product Audit, Process Audit and Internal Audit. Other types of audit is also learn based on requirements.
For audit overview, we usually perform a product audit to check the product is manufacture and meeting all the customer requirements starts from incoming to the final dispatch location. Dock audit is also one of the product verification audit.
The Process audit is conducted for specific process. Which ensures that our process is as per standards or not.
Usually the audits are planned yearly and done accordingly. Audit plan is something we need to follow and perform the audits according to audit check sheets.
Problem solving tool’s.
The most crucial skill that every quality engineer should have is the problem solving. Problem is everywhere in the company, either in process or product defect or inspection process or in raw materials.
The quality engineer uses the problem solving tools to analysis the date, identify the actions, implement the actions and the problem will resolve.
There are many problem solving tools, but below are common and basic tools every quality engineer should know. Try to learn the below tool’s as early as possible.
Step #5: Quality Engineer Skills and Competences
This is the most important step as you need to learn as next level quality engineer. Here in this step, you see all skills and competencies that you should learn in detail for advanced career growth.
Basically, some of the topics we already covered in the above steps but still to link with a full roadmap you will see them below.
As per the ASQ (American Society for Quality) you should know all below topics to be a Certified Quality Engineer. We will list down all topics which are mentioned in the ASQ body of knowledge.
You must know these skills and tools to stand out as Quality Engineer in Organization. Don’t waste your time, let’s jump to the topics.
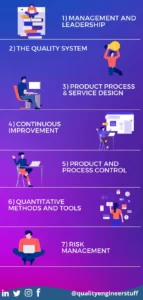
The content is divided into 7 categories.

- Management and Leadership
- The Quality System
- Product Process & Service design
- Continuous Improvement
- Product and Process Control
- Quantitative Methods and Tools
- Risk Management
1. Management and Leadership
- Quality Philosophies and Foundations
- Continuous improvement tools,
- lean, Six Sigma, theory of constraints
- statistical process control (SPC)
- Total Quality management
- leadership principles (including Deming’s 14 points)
- The Quality Management System (QMS)
- Strategic planning
- Deployment techniques
- Benchmarking
- Stakeholder
- Performance
- Project management
- Quality information system (QIS)
- ASQ Code of Ethics for Professional Conduct
- Leadership Principles and Techniques
- Facilitation Principles and Techniques
- Roles and responsibilities
- Facilitation tools
- Communication Skills
- Customer Relations
- Supplier Management
- Techniques
- Improvement
- Risk
- Barriers to Quality Improvement
2. The Quality System
- Elements of the Quality System
- Basic elements
- Design
- Documentation of the Quality System
- Document components
- Document control
- Quality Standards and Other Guidelines
- Quality Audits
- Types of audits
- Roles and responsibilities in audits
- Audit planning and implementation
- Audit reporting and follow-up
- Cost of Quality (COQ)
- Quality Training
3. Product, Process, and Service Design
- Classification of Quality Characteristics
- Design Inputs and Review
- Inputs
- Review
- Technical Drawings and Specifications
- Verification and Validation
- Reliability and Maintainability
- Predictive and preventive maintenance tools
- Reliability and maintainability indices
- Reliability models
- Reliability/Safety/Hazard Assessment Tools
4. Product and Process Control
- Methods
- Material Control
- Material identification, status, and traceability
- Segregation of Material
- Material classification
- Material review board
- Acceptance Sampling
- Sampling concepts
- Sampling standards and plans
- Sample integrity
- Measurement and Test
- Measurement tools
- Destructive and nondestructive tests
- Metrology
- Measurement System Analysis (MSA)
5. Continuous Improvement

- Quality Control Tools
- Quality Management and Planning Tools
- Affinity diagrams and force field analysis
- Tree diagrams
- Process decision program charts (PDPC)
- Matrix diagrams
- Interrelationship digraphs
- Prioritization matrices
- Activity network diagrams (Analyze)
- Continuous Improvement Methodologies
- Total Quality Management (TQM)
- Kaizen
- Plan-do-check-act (PDCA)
- Six Sigma
- Theory of constraints (ToC) (Evaluate)
- Lean tools
- 5S
- Value stream mapping
- Kanban
- Visual control
- Waste (Muda)
- Standardized work
- Takt time
- Single-minute exchange of die (SMED) (Evaluate)
- Corrective Action
- Preventive Action
6. Quantitative Methods and Tools

- Collecting and Summarizing Data
- Types of data
- Measurement scales
- Data collection methods
- Data accuracy and integrity
- Descriptive statistics
- Graphical methods for depicting relationships
- Graphical methods for depicting distributions
- Quantitative Concepts
- Terminology
- Drawing statistical conclusions
- Probability terms and concepts
- Probability Distributions
- Continuous distributions
- Discrete distributions
- Statistical Decision Making
- Point estimates and confidence intervals
- Hypothesis testing
- Paired-comparison tests
- Goodness-of-fit tests
- Analysis of variance (ANOVA)
- Contingency tables
- Relationships Between Variables
- Linear regression
- Simple linear correlation
- Time-series analysis
- Statistical Process Control (SPC)
- Objectives and benefits
- Common and special causes
- Selection of variable
- Rational subgrouping
- Control charts
- Control chart analysis
- Pre-control charts
- Short-run SPC
- Process and Performance Capability
- Process capability studies
- The Process performance vs. specifications
- Process capability indices
- Process performance indices
- Design and Analysis of Experiments
- Terminology
- Planning and organizing experiments
- Design principles
- One-factor experiments
- Full-factorial experiments
- Two-level fractional factorial experiments
7. Risk Management

- Risk Oversight
- Planning and oversight
- Metrics
- Mitigation planning
- Risk Assessment
- Risk Control
- Identification and documentation
- Auditing and testing
- Failure and Mode Effect Analysis (FMEA)
Hope all the details are covered in this article. In future articles, you will learn the detailed concept for each tool and topic. If you want to get updates on the latest content please subscribe to our newsletter, It is free.
Please share the content with your friends and colleagues, so that it will help others to learn.
