Hi Quality Engineer, You have heard in your organization about the internal quality audit notification. That management is planning the IATF internal audit and you need to face the audit.
But before that, you must know about what internal quality audit is? and what is the procedure for the same.
Internal quality audit helps to improve business processes and product quality, which are highly challenging and customer focus to drive the business.
IATF internal audit is very important to ensure our organization is compliance to standards, regulation and continual improvement as a automotive company.
By following this complete guide you will learn detail concept, formats, documents, terms and procedure of internal quality audit. If you finished this complete guide you are one step ahead in your documentation journey.
This complete article helps you to know everything about internal audit concept.
So, let’s dive in.

What is Internal Quality Audit (IQA)?
The internal quality audit is the process for verification and ensures the performance of the organizational Quality Management System. It can help to monitor and check that organization is meeting standard requirements.

It is the documented activity, where verification and evaluation of objective evidence are done. The final goal of this audit is to collect information about the effectiveness of our quality management system (QMS).
So, there are some guidelines of internal audit such as Who is perform? How does it perform? etc. for this let’s see the complete procedure of internal audit.
What are the documents requires for IATF Internal Audit?
Following documents required for IATF Internal Audits
- IATF 16949:2016 Standard: This is a core document of automotive QMS requirements.
- Internal Audit Procedure: Documented procedures shows how internal audits are planned, conducted, reported, and followed up.
- Audit Checklist: A detailed checklist aligned with IATF 16949:2016 requirements.
- Audit Plan and Schedule: Scope, objectives, criteria, and schedule of internal audits.
- Audit Reports: Reports summarizing audit findings, conclusions, and recommendations for corrective actions and improvements.
- Non-conformity Reports: Documentation of non-conformities, including root cause analysis and corrective actions.
Why we do Internal Audit?
1. Compliance: Ensure the organization fulfill IATF 16949:2016 standard requirement, which are mandatory for automotive quality management systems.
2. Continuous Improvement: This audit finds out the area of improvement for our processes, products, and system. This will overall improves our efficiency and quality.
3. Risk Management: Internal audit verifies our production processes and supply chain activities for risk assessment and measures. It will help to reduce those risks.
4. Customer Requirements: IATF standards focus on to meet customer-specific requirements and their expectations. Therefore, IATF internal audit will helps to find out the gaps in our organization.
How to do IATF Internal Audit?
Step #1: IATF Internal Audit Planning:
Prepare an internal audit plan which includes when we are going to do the internal audit. This considers the frequency of audit.
Decide the frequency of audit. It should be the documented file that includes all the QMS related processes/department requirements. Some organization plans the IATF internal audit Yearly once and some plan Half-yearly.
QMS standards basic requirement is to do at least once in a year. Depending on issues and non-conformities organization decides their own frequency.
Define Audit scope: Define the scope of the audit. The Audit scope considers what processes, which departments, and which locations need to be audited. It should cover all the functions/departments relevant to QMS scope.

Additional audit can be planned depending on certain conditions with the discussion of a responsible person. the conditions are
- If there are many non-conformities in a particular function/process.
- Change in manufacturing process
- frequently customer claim for any function/process
Mention in the plan that if the audit is not performed as per schedule due to any critical situation, then the audit will be re-schedule within a month or ASAP.
Step #2: Internal Audit Schedule
After making plan once the audit time closer then prepare audit schedule.
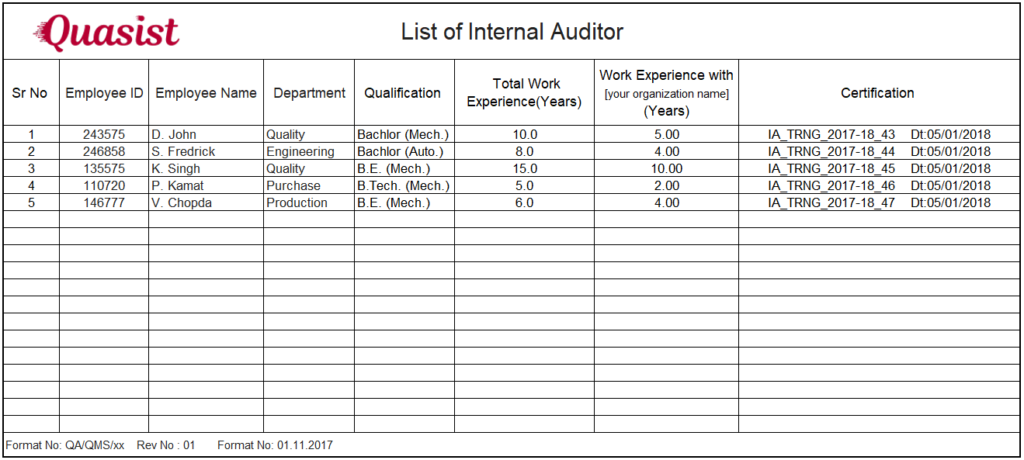
Internal Auditor’s List: Consider the skilled internal auditors for the audit program. The list of certified internal auditor will give you the name of auditors who have undergone the training of IATF 16949:2016 auditing techniques and become a IATF Certified Internal Auditor.
There must be a qualified internal auditor in the list. Make sure auditor should not audit their own work. This one is Mention in the standard, which Auditor you should refer.
Audit Scheduling: This audit scheduling consist of list of processes or departments along with their audit scope. Then who will be the auditor of respective process and who will face the audit (Auditee/process owner). Also includes the scope, date and time of the audit.
In short audit schedule means when audits will be performed and who and how will take the audit.
It is mandatory, that all working shifts must be audited. It must include in the Audit schedule.

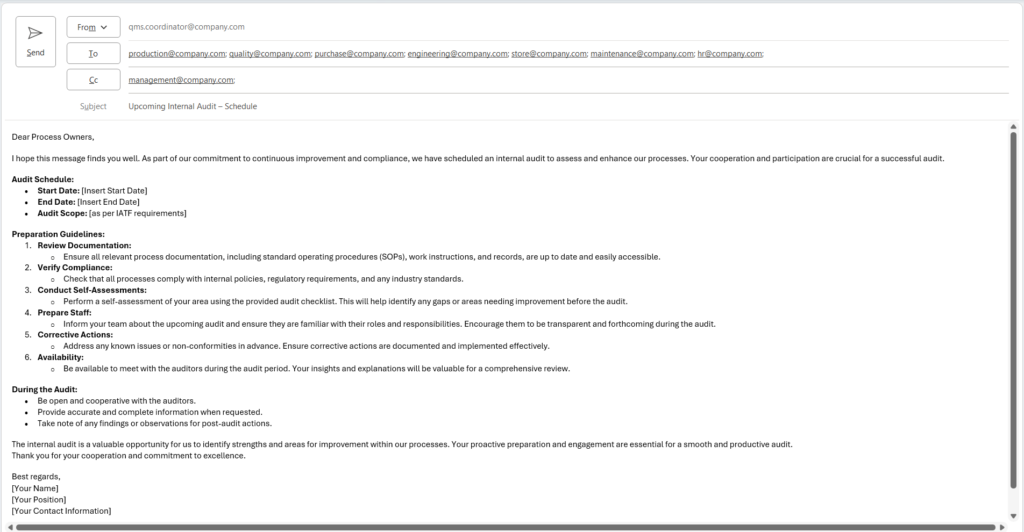
Audit Communication: Notify and Communicate all the departments, functions and process owners this audit schedule. It should be our common courtesy to inform about upcoming audits. It will help the Auditee to prepare required documents and pieces of evidences.
Basically, best way of communication made through mail communication or any other suitable channel whatever you choose.
Refer below email template of how to communicate audit schedule in organization.
Step #3: Internal Audit Preparation
The auditor conducts audit as per clause requirements of respective function/Scope as scheduled.
Document Review: Collect all relevant documents such as the IATF 16949:2016 standard, internal procedures, process maps, and previous audit reports. This will have clarity on baseline for audit.
Internal Audit Checklist: Prepare an audit checklist based on the IATF standard’s requirements and any other organizational criteria. This checklist gives the outline of audit scope. And helps auditor to do audit in systematic way.
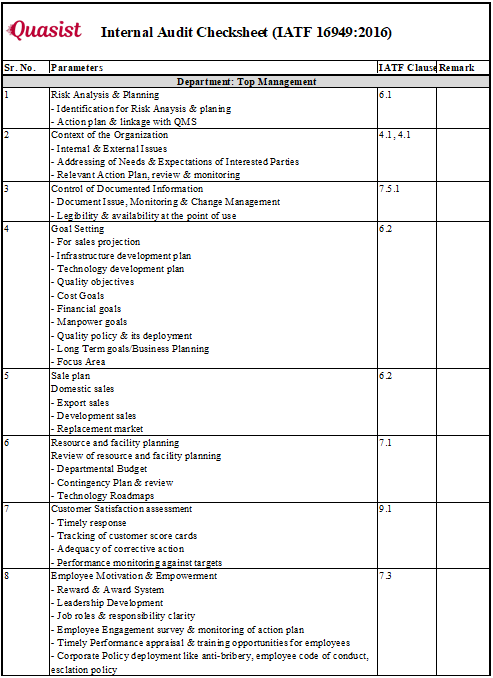
Step #4: Conduct IATF Internal Audit
Opening Meeting: Introduce the audit team, explaining the audit objectives, audit scope, and method to auditees.
Conduct IATF Internal Audit: Perform actual audit by knowing processes and ask for evidences as per audit checklist. Review all documentation and check for compliance and standards.
Auditor shall use any or combination of auditing techniques like observing, questioning, interviewing the auditee for verification, and recording the objective evidence of conformance or non-conformance in the audit report.
It is very important to ask the right question to the right people at the right time. You must have a good Auditor quality for successfully completing the audit.
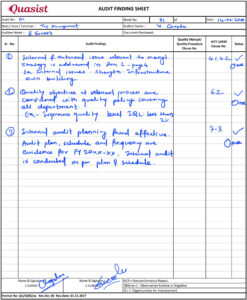
Record Internal Audit Findings: Document all your observations in the audit finding sheet or observation sheet. Kindly fill the audit finding sheet with all evidence verified and what is the conclusion on this point.
Internal Audit NC Reporting: All the non-conformities are report in the Audit report. During an audit, the auditor may find some deviations, or some requirements are not meet to standards, this should be report as non-conformity.
Record all non-conformities in audit finding sheet. The type of non-conformity (NC) includes Major NC or Minor NC or Opportunity for Improvement/area for improvement.
Auditor shall investigate customer, government management & standard requirements while auditing. Auditor shall also identify the areas of improvement and report them as observation.
A closing meeting should be plan by auditors to summarize all audit findings.
Audit Closing Report & Internal Audit NC communication: Discuss audit findings with auditees and team, have clarification on any misunderstandings, and confirm actions to be taken. This process is important because after audit everyone agree to all observations and NC’s. All Non-conformities discussed and communicated through NC report along with audit closing report.
Step #5: Internal Audit Reporting and Follow-Up
Audit Report: Prepare a detailed audit report with all audit summary of findings, conclusions which includes non-conformity and best practices, and recommendations such as area for improvement.
Non-conformity Management: Non-conformities identification, classify them based on severity, and ensure corrective actions are proposed and implemented within timelines.
Follow-up Audits
Plan and schedule follow-up audit to verify effectiveness of corrective actions and improvement points.
Follow-up audits are perform on the non-confirming audit findings. But it depends on the auditor that he just wants to audit only NC points or complete function again.
Preferably, the same auditor shall carry out the follow-up audit of the department after the commitment date or during subsequent audit day and shall record the findings on NC copy.
Step #6: NC closure and Audit Closing summary
Depending on the NC type and their action plan, after doing the follow-up and checking effectiveness auditor can close the NC. Once all NC are closed the audit closing summary need to be done.
Step #7: Continuous Improvement
Finally, do audit analysis to evaluate the continuity, stability and effectiveness of the Quality Management System (QMS).
Do detail analysis of audits and prepare for management review.
Management Review: Present audit results to top management in management review meetings (MRM). Usually in this meeting management will take decision to improve quality system. And sometimes dedicated responsible and resources can be allocated do this improvement initiative.
Process Optimization: Use this audit findings and results to improve processes, increase product quality and achieve operational excellence.
Conclusion
By following these perform internal audit steps and ensuring the availability of necessary documents, organizations can effectively conduct IATF internal audits to fulfill legal & compliance, initiate continual improvement, and meet automotive industry standards and customer expectations.
The next step is to follow the roadmap so that you will learn the concept in the actual sequence that every Quality engineer should go through.

I am a full time Engineer and Quality Professional with over 11+ years of experience in the automotive industry. My professional journey has started from a small enterprise quality inspector to a advanced quality expert. I am creating a good-quality content for engineers. Help them to grow in their career.Learn more here.