Hi.. Let’s take a look for what is welding? Types of welding processes…
What is welding?
Welding is the metal joining processes which produce merging of material by heat them at require temperature, with or without the application of pressure or filer material, so that they can be fuse together. Therefore heat is the major factor of welding processes so that the metal get fuse together.
Example of the welding :- from ancient techniques, they use to heating & hammering to join the separate pieces of iron this same forge welding technique is the only known for the centuries earlier. The more use of welding & its platform made during the world war. As we have lot of welding techniques and it’s processes, still in developed to these days.
Welding Principle
A welding can be defined as coalescence of metals produced by heating to a suitable temperature with or without the application of pressure of, and with or without the use of a filler material.
So there are the standards for the joining of the metal pieces, called as welding joints, these joints gives the welding strength for the part geometry and profile.
Types of welding
All welding processes covered in two basic categories.
1. Pressure welding or Plastic welding or Solid state welding
Metal parts are heated in plastic state and join together with the help of external pressure. E.g. Resistance welding
2. Fusion welding or Non-pressure welding
The metal parts are heated at jointed state at molten temperature and get solidify.
Classification of welding processes
1. Arc Welding
- Tungsten inert gas
- Metal inert gas
- Metal arc
- Plasma arc
- Shielded metal arc
- Submerge arc
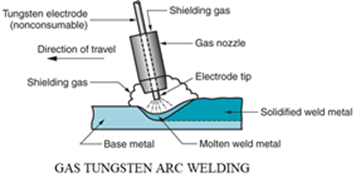
2. Gas welding
- Oxy-acetylene
- Air-acetylene
- Oxy-hydrogen
3. Resistance welding / Spot Welding
- Butt
- Spot
- Seam
- Projection
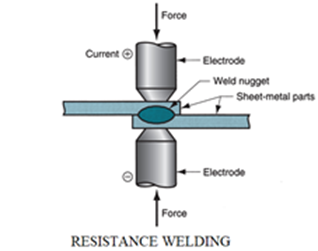
Spot welding is one of the oldest welding processes. It is use in a wide range of industries, specially for sheet metal assembly for vehicle bodies.
4. Solid state welding
- Diffusion
- Friction
5. Electron beam and Laser welding