Hì, hope you have read our article on FMEA Fundamentals and AIAG-VDA DFMEA guide. That article was liked by many people, and contact us to make the guide on PFMEA also.
So, this article is a complete guide on the AIAG VDA PFMEA (Process FMEA) topic.
There are few companies that are doing the DFMEA because not everyone has their own design. Therefore DFMEA is not applicable to them,
But every manufacturing company is responsible for the process. And they have complete control over the quality of the product, and what they are producing.
That is why many people are familiar with and aware of the Process FMEA skills.
Now there is a requirement for the creation of PFMEA according to the new AIAG VDA 2019 first edition standard.
So, this article covers the entire PFMEA procedure as per the new AAIAG VDA PFMEA method.
Let’s dive in,

What is the Purpose of PFMEA? #
First, the long form of the PFMEA is Process Failure Mode and Effect Analysis.
We already discussed that every manufacturing company is responsible for producing a good quality product.
In this competitive market product quality is everything. It means there is no defect or failure in the product.
So, to avoid those future failures in the process we do the risk analysis. PPMEA is one of the risk analysis tools and is used to identify potential failure in the early process development stage.
Therefore the purpose of PFMEA is to identify and reduce the risk of process failures in an early stage of development.
Next, we will cover the entire execution part.
How to create the AIAG VDA PFMEA? | Execution of Process FMEA #
The PFMEA is executed by a 7-step AIAG VDA methodology. The steps are mentioned below,
- Planning and Preparation
- Structure Analysis
- Function Analysis
- Failure Analysis
- Risk analysis
- Optimization
- Result Documentation
Further, we will go through all the steps as how to create a complete PFMEA step-by-step method
Step 1: Planning & Preparation #
In this step, you generally get clarity about the PFMEA project.
Which covers the project scope and preliminary inputs to understand the product and process.
PFMEA scope: #
This covers the basic know-how about our product. What do we need to consider and what is not?
Which product is we are using for our study? For example is it the final assembly or any sub-assembly is in our FMEA scope
Project Plan: #
This is the plan we need to create using the 5T’s method. This will help us to get the complete picture of our PFMEA analysis. What, Why, How, and When we will do it?
5T are as below,
- Team
- InTent
- Time
- Tool
- Task
We have explained the complete concept of project planning using the 5T method in different articles.
PFMEA Header: #
This PFMEA header is required to fill in the initial information related to the PFMEA project.
This usually includes the details about the product and some key points which is important to distinguish the PFMEA from others

Inputs: #
Some other generic inputs is also required to start the PFMEA activity. Which includes,
- Customer-specific requirement
- Process standards
- Legal documents
- Drawings 2D/3D
- Manufacturing Layout plan
- Assembly bill of material (BOM)
- Etc.
Here our planning and preparation step ends. The next step will be structure analysis.
Step 2: PFMEA Structure Analysis #
In the structure analysis stage, you need to create the operation map as a structure.
This will provide you with a complete visualization of your process operations.
Process Flow Diagram is the important input you should consider to do the structure analysis. All process steps in our scope should be included in the structure analysis.

There are three levels of structure in PFMEA structure analysis.
Process Item | Process Step | Process work elements

The Process Item: #
This is the final output of our processes. When all process operations are completed then you will get the final product which is nothing but your process Item.
Process Item could be your final assembly. lt can be the sub-assembly which is only in your PFMEA scope.
Process Step: #
This is the actual workstation operation on which a particular process is to be done
In our process flow diagram we identify our processes as OP10, OP20, OP30, etc. with detailed description.
Then the one OP is your process step. You need to do the PFMEA for further analysis to OP wise.
Process Work Element: #
The work elements needed to perform the process step/OP is the process work elements
The work elements are our 6M work elements.
- Man
- Machine
- Material
- Method
- Environment
- Measurement
When we say our process operation is robotic welding operation then, we require a man to start the welding, a robot is a machine to performs welding. Then weld wire and shielding gas are required which is considered as a material, close working environment is needed.
Describe the complete picture view of welding and work elements.
In this way, you need to think about which process work elements are required to perform the process step.
So, the final structure analysis looks like below for our example

Step 3: PFMEA Function Analysis #
The function meaning is what the process/assembly is intended to do.
We had done our structure analysis.
Now, each structure element such as process item, process step, and process work elements should have functions We need to identify the functions for the same.
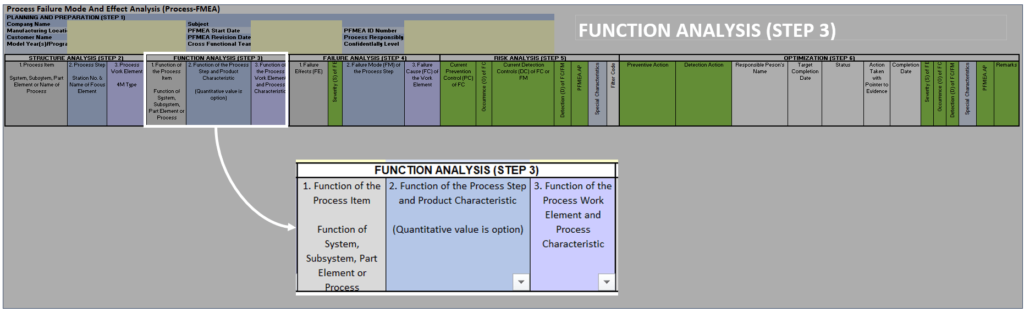
How to identify functions in PFMEA? #
Let’s talk about each element’s functions
Process item functions: #
The function of the process item is the top assembly-level function.
This may include the functions from the DFMEA so that we are taking inputs from DFMEA to PFMEA.
These also may include some customer requirements, legal and safety functions/requirement
Usually, the functions of Process Item are categorized into below levels
- Functions at Your plant
- Functions at the Customer end
- Functions at End-user
Function of Process Step: #
The process step is the operation, therefore you need to write the function as what this process actually does.
Also, you can add the product characteristics as the function which is the output of the operation performed.
Functions of Process Work Element: #
You know the work elements are nothing but our man/machine/material/method which is needed to perform the respective operation.
Therefore the functions of the work element are nothing but what the work element does in the operation
What man is doing is the function of man
What the machine is doing is the function of the Machine
Sometimes the process characteristics are also added to the work element function
Process characteristics are the requirement of the process work element.
Refer functions analysis tree for the steps of process item, process step and process work elements.

After the function analysis, we do a failure analysis
Step 4: PFMEA Failure Analysis #
Failure analysis is the heart of the FMEA study. If you identify the correct potential failures then you will reduce the risk effectively.

How to identify the failures in PFMEA? #
Till now you have identified the functions of the process item, process step, and work elements
Now for those functions, we need to identify the failures. So failures are either negative of the functions or non-fulfilments of function.
How the function failure will give you the correct failures and then you can logically link those failures as a cause, mode, and effect relation.
In case you have identified the product or process characteristics then the failure of those characteristics is your failure
Failure Mode: #
The failure of the process step functions is the failure mode
Failure Cause: #
The failure of the process work elements is considered a failure cause
Failure Effect: #
The failure of the top assembly functions in your plant or customer end or end user level will be the failure effect.
After logically linking those failure effects, failure mode, and failure cause you can have a good picture of failure analysis
You can say we have the failure mode in our process step. This failure mode occurs due to the failure cause of process work elements, And once the failure mode is produced, as a consequence the failure effect happens on the process item.
Refer below example of the failure analysis,
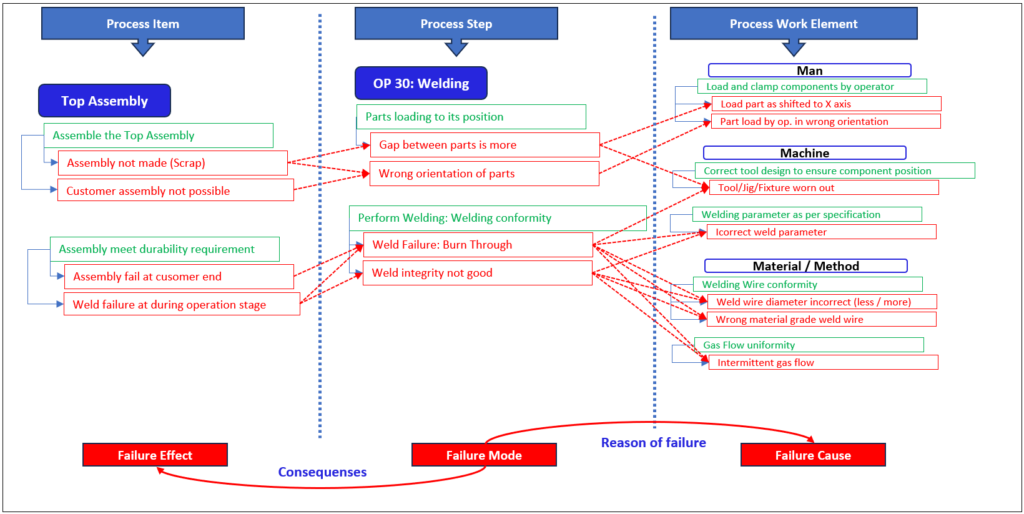
Failure analysis is completed now. The next step will be your risk analysis.
Step 5: Risk Analysis #
The purpose of the PFMEA risk analysis step is to identify the risk based on failures and their controls
The sub-activities in the risk analysis include are,
- severity rating
- provide the prevention control
- occurrence rating
- provide the detection control
- detection ratings
- identify the risk
Let’s see how the risk analysis is working in detail
Severity Rating: #
The severity rating depends on how big is impact of the failure effect is.
See the table to mention the severity rating below, and choose the level depending on the criteria of failure effect.
Severity data is to be linked from the customer to DFMEA first. Then the DFMEA severity is transferred to PFMEA based on the failure effect from DFMEA
This will ensure our design risk management throughout the development process from customer to supplier to sub-supplier.

Current Prevention Control: #
The current prevention control is the actions that we take before process operation
Refer to prevention controls as an example below,
- Work Instructions,
- Set-up Approval,
- Preventive Maintenance,
- Poka-Yoke (Sensor, Mechanical, etc.),
- Automated controls
- etc.
These controls usually prevent failure from happening These actions we generally considered before the start of the process operation.
Occurrence ratings #
How frequently or the frequency of the failure causes occurrence based on how strong the prevention is defines the occurrence rating
It is like you have identified the current prevention controls for the cause. And how strong our prevention is to prevent the failure cause from happening. This is the exact level you need to select from the table.
You can refer to the occurrence table for the ratings and levels below.

Detection control: #
Detection controls are the action to detect the failure cause or failure mode
Once our process operation is done, we need to verify our output using some inspection methods. These actions are to be considered as detection controls.
The detection methods can be automatic, manual, or visual.
we need to validate our design using some tests and procedures, those actions are considered as the detection control.
Refer to process detection control as an example below,
- In-process inspection
- First-part inspection/First-off/last-off part check
- Gage measurement
- Visual check
- Automatic detection
- Etc.
These detection controls are used to detect the failure after the operation is completed and before leaving the part to dispatch or to the customer.
One key point is the consideration is when we identify the prevention controls it will be for failure cause. And when we identify the detection controls it will be for failure cause and/or failure mode both

Detection ratings #
The level of how strong our detection action is referred to as the detection rating
It is possible to detect the failure cause and failure mode based on detection controls
You can refer detection table as a detection rating guideline below,

How to identify the risk in PFMEA? #
You have done all activities which require for risk analysis.
Now it’s time to analyze the risk based on the data we have. As per the new AIAG-VDA standard this risk we called as Action priority in FMEA
Action Priority: #
earlier we were calculating the risk based on the RPN method. Which was the multiplication of Severity x Occurrence x Detection.
But, AIAG VDA PFMEA we are using a Action Priority new way of identifying the risk is Action Priority.
Still, the action priority is dependent on what is severity, occurrence, and detection. To check those values in the table and you will get the final risk
The action Priority is categorized into 3 ways,
- Low (L)
- Medium (M)
- High (H)
You can refer below table to identify the correct Action Priority

Also, you can learn the detailed guide on Action Priority, so that you will have a better understanding of the new concept.
Step 6: Optimization #
Till now you got the risk, either it is High(H), Medium(M) or Low(L)
Now next step is to reduce the identified risk
How to reduce the PFMEA risk? #
The purpose of the optimization step is to reduce the High/H) & Medium(M) risk. So that our process is more robust.
We will reduce the PFMEA risk based on additional prevention and detection measures
When we say additional measures it means we are improving our existing process condition with better controls
We can reduce the risk by using the below measures,
- Improve or add better prevention action
- Reduce the occurrence rating based on additional prevention action
- Improve or add better detection action
- Reduce the detection rating based on better detection control
- Sometimes you will make major changes in the process it can be a way of reducing the risk.
Optimization Step Columns #
There are some columns of optimization steps as below,

Prevention action: #
Additional Prevention actions to improve the process
Detection action: #
Additional Detection action to improve the process
Responsible person’s name: #
The person name who is responsible for implementing the action. This person also ensures the effectiveness of the action and the result
The responsible person must communicate the results of actions and ensure that the process is improved or not. Either risk is really reduced or not
Target Date: #
This is the tentative target completion date by which our action will be implemented and closed
Status.
There is a need for PFMEA updates by taking follow-ups of action plans. And regularly update the current status of the action.
The status includes the action is,
- Open
- In-process
- Implementation pending
- Completed
- Cancelled
If you find any action is not feasible to implement and it has been cancelled then it is advisable to keep the action in the PFMEA and make the status as cancelled. Because to maintain the history and for future reference, we need to keep such actions.
Action taken with a pointer to evidence: #
You have defined the actions to improve the process in the prevention and detection column. But to complete the actions what actual activity you have done. Those points you need to mention in the action taken column.
It can be the actual action you have done. It can be some documented evidence you can add.
Sometimes any action is not feasible to implement. In this case, you can mention the reason for not being implemented for future reference.
Completion Date: #
This is the actual completion date for the action. This must be the date when you have implemented the action and effectiveness is verified.
Severity(S): The maximum severity of the failure effects. The same as the severity before.
Occurrence (O): #
This is the revised occurrence rating based on improved or better prevention action in the optimization step
Detection (D).
This is the revised detection rating based on improved or better detection action in the optimization step
PFMEA AP: #
This is the final AP (Action Priority) where you can actually say that the risk is now reduced or is it still the same?
How you can say that the PFMEA risk is reduced? #
let’s take an example here before we have high risk. To reduce the risk we have identified further prevention/detection actions. Based on the revised action the occurrence and detection ratings were reduced. Therefore 2nd AP is with reduced risk.
Step 7: Result Documentation #
This is the final step of the AIAG VDA PFMEA study
The PFMEA analysis is now completed till the 6th step of optimization
The purpose of step 7 is to make and communicate the output of the PFMEA study
As PFMEA is the risk analysis tool, the output is more important from a management and program development point of view.
Also, it is the requirement of the IATF and/or ISO OMS standards
Therefore, we got DFMEA results documentation as an output below,
- PFMEA Form
- High and Medium Risk failures
- Product Characteristics
- Action to improve the process
- Design change recommendations
These all are the outputs we got from the Process FMEA analysis.
AIAG VDA PFMEA Template with example #
Also one of the importance of this step is, to present the PFMEA results to auditors. Because we always face audits.
The audits can be internal, external, customer, or QMS audits. The auditor will always ask the PFMEA and the results
Therefore you are ready to demonstrate and show the results to the auditor if you have done the result documentation step correctly.
Summary of AIAG VDA PFMEA #
Finally, is it clear how you can create AIAG VDA PFMEA?
PFMEA creation starts with the planning step where you can define the scope and collect basic inputs for PFMEA creation. Then structure analysis will give you a better picture of which processes or assemblies we are including in our PFMEA study. We do the function analysis to identify the function of each process step, process work element, and process item. Then we do the failure analysis by the method of how the process functions can fail.
Then the logical linkage of failure and function will help us to understand the failure mode, failure effect, and failure cause relationship. Later we do the risk analysis by defining current prevention and detection control along with the severity, occurrence, and detection rating.
The risk is identified as the action priority of Low (L), Medium (M), and High(H). The next optimization step we perform is to reduce the risk. Lastly, you need to do the result documentation to communicate the PFMEA risk to the management and stakeholders.
Also, you can have a look on the AIAG-VDA Design FMEA guide
Be part of our community by subscribing to the newsletter so that you will get the latest articles in advance.




