
Arc welding is the metal joining processes which produce merging of material by heat them at require temperature, with or without the application of filer material, so that they can be fuse together.
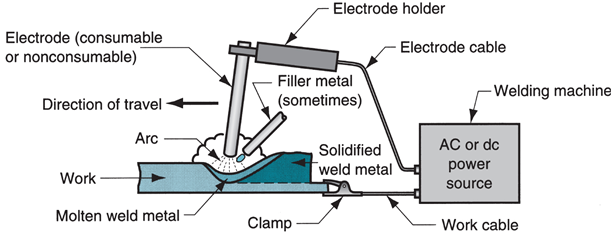
The main function of the arc is to produce heat & melt the base metal surface and the filler metal electrode. The electric energy of the arc produces the heat with the temperature ranges from 2800°C to 20000°C which is enough to melt the any metal surface to be weld. In arc welding processes mostly filler metal is used to achieve the high strength of the joint and to increase the volume of the joint.
The electric arc plays the main role in arc welding to produce the heat. Electric arc means the electrical discharge of a gap between electrode and circuits. To generate the arc, operators do contact the electrode with the work piece and take separate it quickly to activate the arc. Arc welding is commonly used types in welding processes. Learn more about the Welding.
There are two basic types of electrode to produce the Electric arc #
1. Consumable Electrode #
This is consumed / used in welding as filler material. The electrode mainly used in the form of wire spools, which is used continuously to avoid interruptions. The electrode melted and added on joints for weld as filler material.
2. Non-consumable Electrode #
This is not consume in welding; additional material is use as filler material. The non-consumable electrode is made from tungsten. Which have the higher melting point and use to produce arc, adding another filler material to be melt in that arc and add on weld joints. Filler material is used in the form of sticks of length.
Types of Arc welding processes #
- Tungsten inert gas
- Metal inert gas
- Metal arc
- Plasma arc
- Shielded metal arc
- Submerge arc




