Lets Elaborate the AIAG FMEA (Failure Mode & effect Analysis) template, we have both Design & Process FMEA (Failure Mode & Effect Analysis).


1. FMEA NUMBER :
Enter the FMEA document number, which may be used for tracking. And a unique identification number for FMEA.

2. System & Sub System :
Indicate the appropriate level of analysis and enter the name and number of the system, subsystem or component being analyzed.

2. Part No., Part Name :
Indicate the appropriate level of analysis and enter the name and number of the system, subsystem or component being analyzed.

3. Model :

Enter the intended model and vehicle line that will utilize and/or affected by the design / process.
4. Core Team :
List the names of the responsible individuals and Departments which have the authority.


5. Drawing No. / Revision No.:
It is the cell for the latest drawing release no. and the revision status of the part drawing for which the FMEA is made.

6. Design / Process Responsibility :
For Design enter the OEM, Department and group. Also include the supplier name if known, and for Process enter the name of manufacturer / Process owner.

7. FMEA Date :
Key date is the initial FMEA due date before which the FMEA should be completed. Therefore in case of Design FMEA the key date should be before release date for production and in Process FMEA it should be before the PPAP submission or SOP date.

The next FMEA date is the date where the original FMEA completed and release.
8. Prepared By :
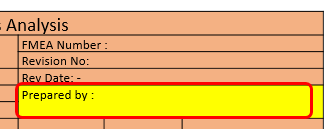
Enter the name of facilitator / the group / person who prepare the FMEA.
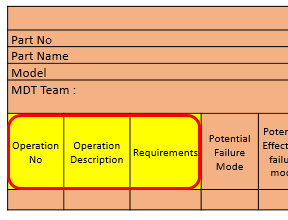
9. Operation no., Description & Requirement:
For Process FMEA we have to enter the operation number as per the sequence in process flow. Write the operation name / process name / Description in respective column. Then enter the process/ operation requirement in 3rd column.
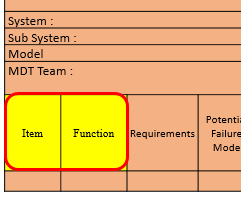
Item/Function :
For Design FMEA, enter the name and item being analyzed and show the design level as indicated on drawing. Enter the function of the item to meet design intent. Include environment issues (e.g. Temp., pressure, humidity etc.) If the item has more than one function with different potential modes of failure, list all the functions separately.
10. Potential Failure Mode :
Identify and list the each failure that could potentially fail to meet the design intent. A recommended starting point is a review of past things gone wrong, concern reports and group brainstorming.
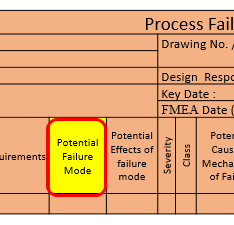
11. Potential Effect of Failure Mode :
Identify the effect of the failure mode on the function as perceived by the customer. It is stated in terms of the specific system, subsystem or component being analyzed.
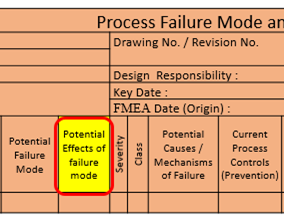
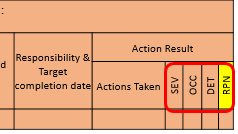
12. Severity (S) :
It is an assessment of the seriousness of the effect of the potential failure mode to the next component, system, subsystem or customer. Severity applies to the effect only. A reduction in severity ranking index can be affect only through a design change. It could be estimate on a “1” to “10” scale.
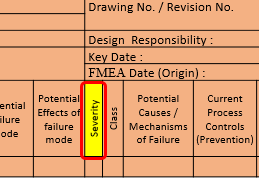
Severity is the value associated with the most serious effect for a given failure mode.

13. Classification :
Classify any special product characteristics (e.g. Critical, key major, significant) for components, subsystem, system that may require additional process controls. Each item identified here in Design FMEA should have the special process controls identified in the Process FMEA.

14. Potential causes of failure :
It is an indication of a design weakness, the consequences of which is the failure mode. The cause should be listed so that remedial efforts can be aimed at pertinent causes.
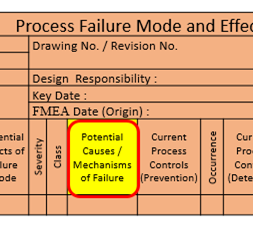
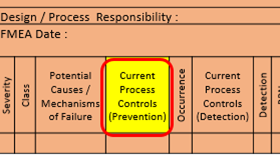
15. Current Design / Process Control (Prevention):
List the prevention, design validation/verification (which will assure the design adequacy for the failure and cause under consideration. There are 3 types of design controls : 1) Prevent the cause or failure mode effect from occurring or reduce 2) Detect the cause and lead to corrective action and 3) Detect the failure mode.
- Avoid failure cause if possible, otherwise avoid failure
- Actions apply to design and not to hardware
- Actions assure observation of specifications
16. Current Design / Process control (Detection)
- Detection of failure cause
- Tests apply to assembly or parts (Hardware)
- Tests according to fulfillment of function and not to fulfillment of specification

17. Occurrence :
The value for occurrence evaluates the likeliness with which the cause can occur. Which results in generation of a failure mode. If the evaluated product is a new
development and there are no warranty cases the value for “Occurrence” will have to be rate.
according to experiences from former projects.

A value of 10 means that the likeliness of
occurrence of failure cause is high, like if it is a new technology.
Occurrence ranking table as per AIAG is as below

18. Detection :

Detection column is for the rank associate with the best detection control list in the Current Design / Process Control detection column.
This detection ranking table as per AIAG as below,

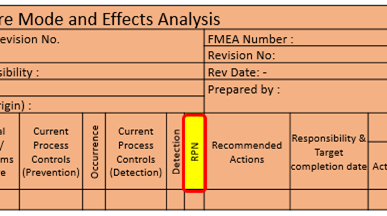
19. RPN:
The RPN is evidence as the risk of a failure / a failure cause.
Severity x Occurrence x Detection = Risk Priority Number
- If the RPN is higher than a threshold-value (specified by customer or internal specification) there must follow an optimization, including one or multiple actions, to lower the risk and with that the RPN. so If the revaluation is not successful, the team will have to arrange a new action if the value of RPN is above the defined threshold-value.
- Occurrence and detection are independent from each other.
- A FMEA report summarizes the knowledge of a development team of the product, system or process and the risk assessment of the design.
- It is important to know that FMEA reports are not being issue to customer as it contains expertise of the company.
19. Recommended Action(s) :
The recommended action is the action taken on highest RPN’s, to reduce the respective occurrence & severity ranking.
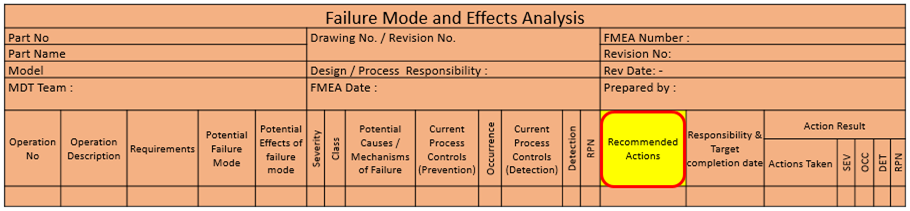
20. Responsibility :
Enter the organization and individual responsibility for the recommended action and the target completion date.

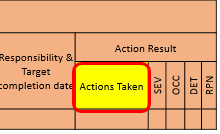
21. Action Taken :
After the recommended actions has been implement, enter a brief description of the actual action and effective date.
22. New RPN :
After the corrective action identified, estimate and record the resulting severity, occurrence and detection rankings to calculate resulting RPN.